Teldat Training
Customized training courses tailored to the needs of each client.
In-Person Certifications
Integra-T unveils an in-person certification offering that covers the full range of technologies marketed by our company.
In order to adapt to routers users’ training needs, teldat is offering students face-to-face Teldat certifications. In this way, the student will acquire adequate knowledge of the technologies our routers use, following a curriculum developed by those responsible for the Teldat product, and taught by fully qualified teaching staff.
During the course, the teacher will create a study and learning plan for the student, solving questions raised by the student during the teaching. Interaction with other students will allow the student to broaden his/her knowledge of the different work environments.
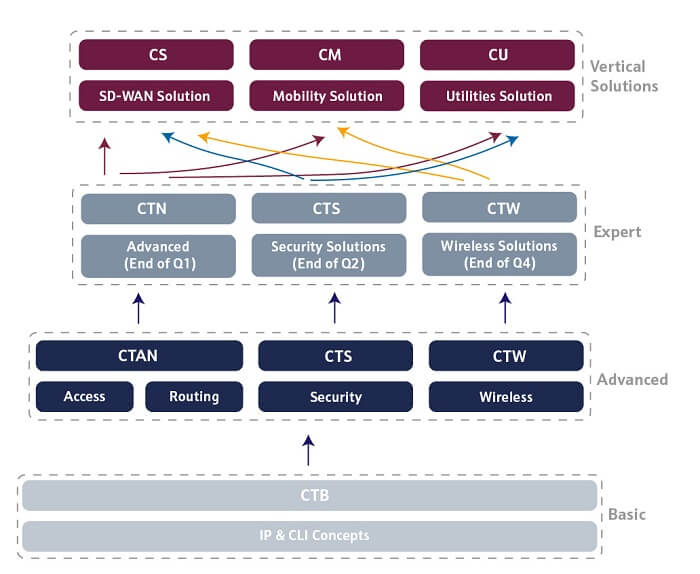
The in-person certification offering covers the full range of technologies marketed by our company. This offer provides various levels of certification:
Basic
This training is mandatory and must be completed to receive any certification. It will give us a basic understanding of networks, communications and the IP protocol, and shows us the CLI structure of our router.
- IP and CLI concepts: This course will provide adequate knowledge on; IPv4, OSI layers, MAC, IPv6, BIOS menu, updating software, managing the device through the configuration, monitoring, and event-and trace-based troubleshooting.
Advanced
This basic training course (CTB) must be passed in order to undertake this training. Each course consists of a theoretical and practical part. In the theoretical part, the student will be introduced to theoretical knowledge about the different technologies, while in the practical part he/she will apply the theoretical knowledge gained to Teldat routers. The available modules are:
Networking (CTAN): The CTAN is the union of two differentiated courses. The student will learn the interfaces, protocols and facilities most used in IP networks. These two courses are:
- Access: This module will introduce the different network access interfaces and technologies and show how to configure, monitor and troubleshoot them.
- Routing: This module focuses on the routing protocols used by the router to route packets. You will see how to configure, monitor and troubleshoot them.
-
- Security (CTAS): This module presents the technologies that the router provides to ensure secure communications. You will analyze tool functioning and tool functionality within the router.
- Wireless (CTAW): This module will show and analyze a WLAN operation, with different work modes.
Expert
The student must pass the necessary assessments (as described in the Certification Program Organization Chart) before taking this certification. The training is a purely practical and the student will recreate a set of scenarios involving different technologies.
- CTN (Teldat Networking Certification): The holder of this certification will be accredited as trained to monitor, control and manage a network. The Access and Routing (CTAN) modules must be passed prior to undertaking this training.
- CTS (Teldat Security Certification): The holder of this certification will be accredited to monitor, control and manage a secure network. The Security module (CTAS) must be passed prior this training.
- CTW (Teldat WLAN Certification: The holder of this certification will be accredited to monitor, control and manage a WLAN network. The Wireless module (CTAW) must be passed prior to undertaking this training.
Vertical Solutions
The student may want to acquire the certifications shown in the Certification Program Organization Chart prior to taking this certification. We have three different certifications:
- CS (Teldat SD-WAN Solution Certification): Teldat has designed SD-WAN precursor products for many years, focusing on developing a solid communications software backed by propietary hardware platforms. Teldat has also perfected automatic installation techniques and worked on overlay projects which enable Teldat customers to configure hybrid Internet/MPLS network. This course will not only show you how to configure and SD-WAN scenario, but also how to use the appropiate tools to manage, control, administer and troubleshoot problems that occur in such scenarios.
- CM (Teldat Mobility Solution Certification): The number of vehicles offering Internet connectivity is rising; so contracting solutions that allow personnel and passengers to enjoy on-board Internet access, while guaranteeing safe browsing and installing tools able routes, will optimize operations and deliver improved user experiences. Teldat provides three SaaS solutions to deliver a complete Wi-Fi solution for your fleet. With this, you can offer a captive portal in your vehicles, filter browsing content and block malware threats. You can also remotely monitor all your devices, tracking their location and obtaining information on the received signal quality.
- CU (Teldat Energy Utilities Solution Certification): Smart Grids consists of the integration of energy grid entities and advanced information systems to benefit electricity suppliers, distributors and consumers. Communications in Smart Grids need to be robust, secure, manageable, and standards-based to ensure connectivity with other network elements. Their main function is to connect the large amount of data in the power grid to data processing systems and decision-making centers, empowering electricity operators by helping them to optimize their generation, supply and demand processes.
CTB Certification
Certification composed of a single course called IP and CLI Concepts. A knowledge of office automation is required to undertake this certification. The course lasts 5 days. A knowledge test consisting of two exams, one theoretical and the other practical, will be conducted at the end of the course. The student must score above 70% to pass.
Objectives
The main aim of this training course is to provide students basic knowledge to allow them to tackle the different certificates at the same time as they acquire the following knowledge.
- Basic concepts of IP and the TCP/IP stack.
- Knowledge of networks.
- Basic Teldat router administration.
Content
Module 1: Introduction
1. Numbering systems
- Decimal to Binary Conversion System
- Binary to Decimal Conversion System
- Hexadecimal to Binary Conversion System
- Binary to Hexadecimal Conversion System
- Hexadecimal to Decimal Conversion System
- Decimal to Hexadecimal Conversion System
- Units of Mearurement
- Network Speeds
2. OSI Layers
3. Types of Protocols
4. TCP/IP Stack
Module 2: LAN Technologies
1. Broadcast and Collision Domains
2. MAC Addressing
3. Fundamentals of Ethernet
4. Introducing VLANs
5. Physical Topologies
6. Network Modules and Connectors
7. Ethernet Standards
8. Introducing ARP
9. IPV4 Header
10. Introducing IPV4 Classes-Classful
Module 3: WAN Technologies
1. WAN Networks
2. Introducing ATM
3. Introducing DSL
4. Introducing DSL Infrastructure
5. Introducing ADSL/ADSL+
6. Introducing VDSL
7. Introducing Cellular Technologies
8. Introducing Cellular Infrastructure Elements
Module 4. Routing
1. Basic Requirements to understand Routing
2. An Introduction to Routing
3. Gateways
4. The Routing Table
5. Step-by-Step Routing
6. A Comparison of Routing Protocols
Module 5: Teldat Routers
1. BIOS Functionalities
2. Accessing the BIOS Menu
3. BIOS Operations
4. Router CIT
5. Distribution File
6. Updating Software
Module 6: Router Administration
1. Accessing the Device
2. Configuration
- Configuring General Device Settings
- Templates and managing their execution
3. Monitoring
- Monitoring the device
- Monitoring interfaces
4. Event System
- Enabling Events
- Events-Filtering and Notifications
5. Teldat Router’s Sniffer
Module 7: IP Protocols applied to the Teldat Router
1. Basic IP Configuration
2. Static Routing
3. DHCP Client-Server
CTAN Certification
Certification composed of two courses, Access and Routing. Each course lasts 5 days, and a knowledge test consisting of two exams, one practical and the other theoretical, will be conducted upon completion of the two courses. The student must score above 70% to pass.
Prior to beginning the training, the student must have successfully passed the “IP and CLI Concepts” course (CBT) assessment.
Objectives
The course is aimed at those people charged with providing a Level 1 or Level 2 support.
The main aim of this certification is to introduce students to the different access protocols and interfaces used by the router, and the facilities and protocols we use in routing. To attend these courses, you must be able to configure, monitor and understand the problems caused by the connection of the router to a network.
Content
Access course syllabus:
Module 1: LAN Switching
1. Duplex in LAN Networks – Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex
2. Introducing VLANs
3. Configuring Basic VLAN Settings
4. Trunk Links
5. DOT1Q Encapsulation
6. Teldat – Configuring the Access Interface
7. Teldat – Configuring the Trunk Interface
8. STP
9. Storm Control
10. N2 QoS in a Switch
Module 2: WAN Interfaces
1. WAN Technologies
2. Introducing GPRS/UMTS/HDSPA/LTE
3. Introducing DIAL Profiles
4. Configuring and Monitoring a 2G/3G Connection
5. Configuring and Monitoring an LTE Connection
6. ATM Operation
7. ATM Infrastructure
8. DSL Infrastructure
9. ADSL/ADSL+ Signaling
Module 3: Bridge
1. Bridge Interface Operation
2. ASRT Protocol
3. STP
4. Configuring a Bridge Interface
Module 4: Fundamentals of NAT
1. NAT Operation and Types
2. Static NAT
3. PAT NAT
Module 5: QoS
1. Introducing QoS
2. Types of QoS
3. Advanced Parameters
Access course syllabus:
Module 1: Fundamentals of AFS NAT
1. NAT Operationg and Types
2. Static NAT using AFS
3. Dynamic NAT using AFS
4. PAT NAT using AFS
Module 2: TVRP and VRRP
1. Introducing First HOP Redundancy
2. Fundamentals of TVRP
3. Configuring TVRP
4. Fundamentals of VRRP
5. Configuring VRRP
Module 3: Services
1. Introducing DHCP
2. Types of DHCP
3. Router as DHCP Server.
4. Router as DHCP Relay.
5. Router as Client
6. Introducing NTP
7. NTP Operation
Module 4: ACLs
1. Types of ACLs
2. Standard
3. Extended
4. Stateful
5. Monitoring
Module 5: SLA
1. Introduction
2. Control Mechanism
3. NSM
4. NSLA
Module 6: OSPF
1. Basic Concepts
2. Introducing the Router-ID
3. Fundamentals of areas
4. Classifying Routers
5. Establishing Adjacencies
6. Configuring Initial Basic Settings
7. The hello and dead intervals
8. Basic Monitoring
9. Types of Network
10. Virtual links
11. Authentication
12. Network import
Module 7: RIP
1. Introduction
2. Message Structure
3. Configuring Basic RIP Parameters
4. Authentication
5. Timers.
6. Configuring the default route.
7. Configuring Summarization
8. Configuring Filtering
9. Configuring the metric value increase
10. Monitoring
11. Trace
12. Example of configuration.
Module 8: BGP
1. Introduction
2. Types of messages
3. Establishing sessions – FSM BGP
4. Attributes
5. Capablities
6. Update message
7. The decision algorithm
8. EBGP Sessions
9. IBGP Sessions
10. Authentication
11. Route reflectors – reflectors
12. Configuring
13. Monitoring
14. Example of configuration.
Module 9: Multicast
1. Introduction
2. Introducing PIM-SM
3. Configuring PIM-SM
7. Monitoring
CTAS Certification
Objectives
The course is aimed at those people charged with providing a Level 1 or Level 2 service.
The main aim of this training is to introduce students to the different security methods that can be applied to the router, both in terms of access to the router and in terms of creating a secure network. To attend these courses, you must be able to configure, monitor and understand the problems caused by the connection of the router to a network.
Contents
Module 1. Basic Device Security
1. Password Policies
2. Logging
3. Privilege Levels
4. SSH
- Server
- Client
5. SFTP
6. Introducing TACACS and RADIUS AAA Protocols
7. RADIUS
- Configuring and Monitoring Radius
8. TACACS
- Configuring and Monitoring TACACS
Module 2: LAN Network Security
1. DMZ
2. HARDENING
- ACLs
- Firewall (AFS)
3. 802.11X
Module 3: WAN Network Security
1. VPN
2. Cryptographic Protocols
- IDS/IPS
- Authentication
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
Module 3: IP Tunnels
1. Introducing GRE
2. Configuring GRE
3. Static Tunnels
4. Dynamic Tunnels
5. NHRP
Module 4: VPN IPSec
1. Introducing IPSec
2. ISAKMP
3. Modes of operation
4. Authentication
5. PSK
6. Certificates
7. SCEP
8. GDOI
9. GETVPN
Module 5: DMVPN
1. DMVPN Operation
2. OSPF DMVPN Operation
3. RIP DMVPN Operation
4. BGP DMVPN Operation
CTAW Certification
CTN Certification
CTS Certification
CTW Certification
CS Certification
CM Certification
CU Certification
Read our latest Blog Posts
Constraint-Based Electronic Design
"The Constraints". While electronic schematics provide a practical way to represent the components and connections within a circuit, they are ultimately a simplification that overlooks important aspects of how the circuit actually behaves....
Your Features are only as Strong as Your Hardware
In the telecom world innovation has taken the spotlight, opening the doors to new protocols, cutting-edge features, ambitious capabilities like 5G, NGFW, etc. Yet behind the scenes, there's a less glamorous, but equally vital actor: the robust...
Cybersecurity and Smart Networks: Core Pillars of Transport Infrastructure
In an increasingly interconnected world, where digitalization is profoundly transforming the way in which transport systems are managed and operated, cybersecurity has become a critical component to ensure continuity, security, and efficiency. From...